| Dear Readers: This is the latest edition of Notes on the State of Politics, which features short updates on elections and politics.
— The Editors |
How likely is an Electoral College tie?
The 2020 election came fairly close to ending in an Electoral College tie. While Joe Biden won the national popular vote by about 4.5 points, his margins in several key states were much narrower. Specifically, Biden’s 3 closest wins were by 11,779 votes (or .24 percentage points) in Georgia, 10,457 in Arizona (.31 points), and 20,682 (.63 points) in Wisconsin. Had these states voted for Donald Trump and everything else had been the same, the Electoral College would have produced a 269-269 tie, leaving both candidates short of the magic number of 270 electoral votes.
If this ever happens, the U.S. House of Representatives would have to decide the election — we’ll have more about how this would work in tomorrow’s Crystal Ball. But before we do that, we wanted to look at whether there are plausible paths to 269-269 in 2024.
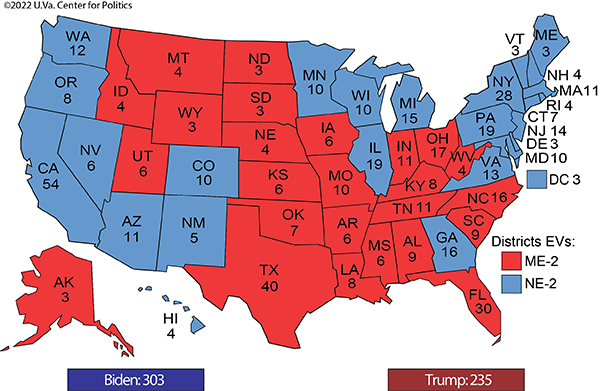
Changes to the electoral vote allocations as a result of the 2020 census have altered the overall math slightly. Using the new allocation based on the 2020 results, the election would have been slightly closer: 303-235 Biden, instead of the 306-232 edge he enjoyed in reality. The 2020 map with the new Electoral College totals is shown in Map 1.
Map 1: 2020 presidential election with new electoral vote apportionment
This also would have changed what would have happened had Arizona, Georgia, and Wisconsin voted for Trump. Under the new allocation, that map would produce a 272-266 Republican victory as opposed to a 269-269 tie.
So the new apportionment of electoral votes alters the potential Electoral College tie scenarios and, as we assess the map, makes such a scenario less likely, because the specific pathway apparent back in 2020 is now closed. But a tie is still possible, even if one restricts hypothetical Electoral College scenarios to only include changes to the states that were the closest in the 2020 election. In other words, one doesn’t have to go to absurd lengths — such as a blue Wyoming or a red Massachusetts — to come up with a tie.
Using 270toWin — our go-to site for Electoral College strategizing — we played around with realistic scenarios for an Electoral College tie. We locked most of the 2020 Electoral College results into place, not altering any states beyond the 7 from 2020 that were decided by less than 3 points (Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Nevada, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin). As part of this scenario, we also locked in the 2020 electoral vote allocations from Maine and Nebraska, the only 2 states that award electoral votes by congressional district. Both states split in 2020, and under the new district lines, Donald Trump would have carried Maine’s 2nd District by about 6 points, with Joe Biden carrying Nebraska’s 2nd District by about the same margin.
So that set a baseline electoral vote floor for each side at 226-219 Democratic, with 93 electoral votes from the 7 most competitive states outstanding. Using these Electoral College puzzle pieces, we came up with 3 scenarios, although scenarios 2 and 3 are very similar.
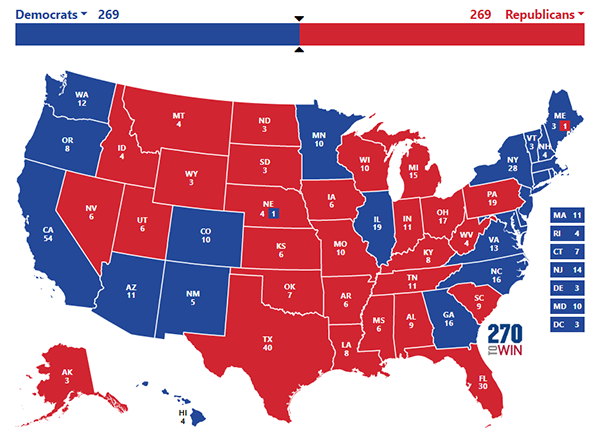
Map 2: Hypothetical Electoral College tie, scenario 1
Map 2 shows the first tie scenario. This one would effectively be a realigning map, where Democrats lose the old “Blue Wall” states of Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin — states that Donald Trump won in 2016 but not 2020 — as well as Nevada, a state that Trump never carried but where Democrats only won by a little under 2.5 points in both 2016 and 2020. Meanwhile, Democrats would hang onto Arizona and Georgia and also flip North Carolina, which was Trump’s closest win in 2020. We don’t find this scenario that plausible because we don’t envision a world in which Democrats are winning Arizona but not its usually bluer northwestern neighbor, Nevada. Nor do we see North Carolina — clearly, to us, the reddest of these 7 states and the only one that backed Trump in both 2016 and 2020 — going blue while 4 of the others go red. The Tar Heel State also is the only one of these 7 states where Democrats had no statewide success in 2022, losing both an open-seat Senate contest and a pair of high-profile state Supreme Court races, making it even harder to imagine it voting Democratic while any of the others are going Republican.
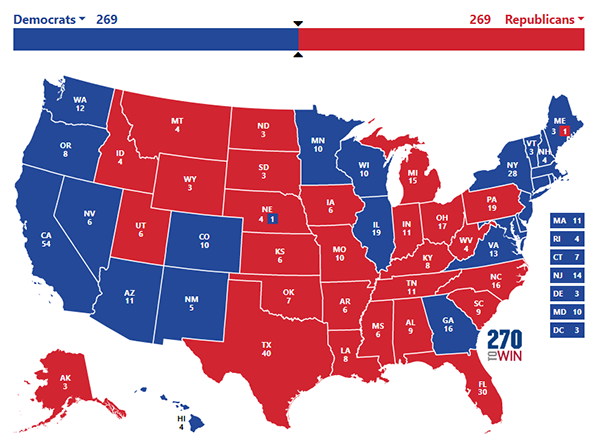
Map 3: Hypothetical Electoral College tie, scenario 2
Map 3 shows another scenario — and this one seems a bit more plausible. Democrats again hang onto Arizona and Georgia. They also keep Nevada and lose North Carolina. All of those states would be replicating how they voted in 2020. Meanwhile, Republicans claw back Michigan and Pennsylvania, but Democrats hold Wisconsin. While this doesn’t require North Carolina to vote blue, it does require Michigan and Pennsylvania to both vote more Republican than Wisconsin, which neither did in 2016 or 2020 (although Pennsylvania and Wisconsin had almost identical margins in 2016). Wisconsin still seems the shakiest for Democrats of these 3 states — Republicans did, after all, defend Sen. Ron Johnson (R-WI) there last cycle and kept the gubernatorial race much more competitive than in Michigan or Pennsylvania, and Biden’s margin was under a point there in 2020. But these states still vote similarly enough that scenario 2 is not out of the question.
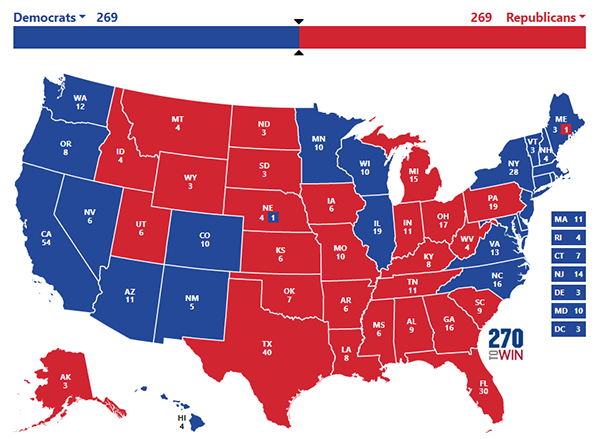
Map 4: Hypothetical Electoral College tie, scenario 3
Finally, Map 4 is identical to Map 3, except North Carolina votes blue while Georgia votes red. This one seems less likely than the second scenario, as Georgia has pretty clearly trended blue in recent years while North Carolina has not.
Overall, an Electoral College tie remains unlikely — landing on a specific 269-269 outcome is something we would not rule out, but we wouldn’t bet on it, either, without getting great odds.
Again, we’ll have more to say about how an Electoral College tie would be decided in tomorrow’s Crystal Ball. But we first just wanted to say that, yes, it’s possible, even under the new Electoral College allocation and even if you just focus on the states that were most competitive in 2020.
Slotkin enters Michigan Senate race
In January, the first Democratic Senate retirement of the cycle came in a light blue state. Sen. Debbie Stabenow, who has held elected office in the state since the 1970s, announced that she would not seek a 5th term. Though Stabenow’s retirement announcement was, in some reporting, considered to be an ominous sign for her party’s prospects, it came at a time of triumph for Michigan Democrats: They had a nearly perfect 2022 cycle. Democrats won most of the marginal House districts, flipped the legislature, and won each of the state’s 3 statewide races with comfortable majorities — their biggest disappointment was the Macomb County-centric 10th District narrowly slipping away.
Surely, with the Michigan Democrats’ large bench, there would be a flurry of candidates ready to get into the open-seat Senate race, right?
Instead, the past several weeks were relatively quiet on that front. If anything, the Democratic “shadow primary” seemed defined by the process of elimination. Almost immediately, Gov. Gretchen Whitmer, who was just reelected to a second term, ruled out a run. Other prominent Democrats followed, with the more notable exceptions of 7th District Rep. Elissa Slotkin and Secretary of State Jocelyn Benson. Though Benson and a few other notable Democrats are still considering the race, Slotkin announced her campaign on Monday.
The Republican field, meanwhile, remains in flux, although Rep. John James (R, MI-10) — the party’s nominee in the 2018 and 2020 Senate races — recently filed for reelection to the House. While that deprives Senate Republicans of a potential recruit, it does give House Republicans an incumbent to seek reelection in a swingy seat next year.
Slotkin, who was first elected amid the 2018 blue wave that crashed in the House, ran after serving in the Obama administration and has a background in the U.S. Intelligence Community. In the House, she has been part of a bloc of center-left Democrats that have taken an interest in national security issues — other examples from the 2018 class include Reps. Abigail Spanberger (D, VA-7) and Mikie Sherrill (D, NJ-11), both of whom could also be future statewide candidates.
Slotkin’s district, which is essentially the successor to a seat that Stabenow held in the late 1990s, is centered on Lansing but extends into the Detroit metro area. Numbered MI-8 last decade, Slotkin flipped the seat by 4 points in 2018 after it gave Donald Trump a 7-point margin 2 years earlier. As Trump carried the district again in 2020, Slotkin replicated her 2018 margin, making her one of only 7 “crossover seat” Democrats that year.
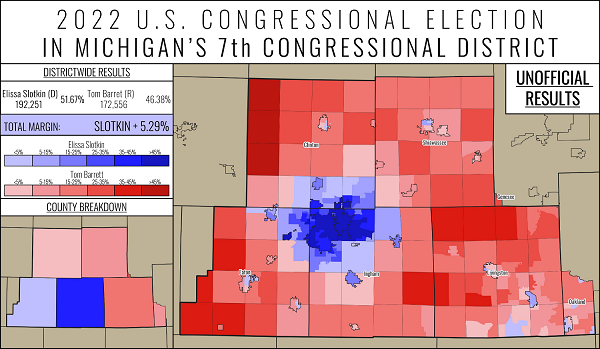
For 2022, redistricting turned Slotkin’s seat into a Biden-won seat, although his margin there was narrow (he would have carried it by less than a percentage point) and it would have narrowly voted against Sen. Gary Peters (D-MI) in 2020. Though the district was a bit friendlier to Democrats, Republican state Sen. Tom Barrett represented much of the area that was new to Slotkin, making him almost a co-incumbent in the race. Overall, the MI-7 contest turned into 2022’s most expensive House race. But as Map 5 shows, the result was a clear win for the (actual) incumbent: Slotkin won a third term by just over 5 points.
Map 5: MI-7 in 2022
Note: Map 5 uses unofficial data, but the official result was almost identical
Source: Jackson Franks
Barrett is running again, and his candidacy could deter other GOP entrants (he was unopposed for the nomination in 2022). Democrats have several prospects for the seat, but it seems possible that whomever they nominate will have a home base in Lansing’s Ingham County — the blue bastion of the district, it gave Slotkin over two-thirds of the vote each time she was on the general election ballot. Aside from running up the score in Ingham County, one of the keys to Slotkin’s electoral success has been keeping Livingston, the district’s second-largest county and the one directly east of Ingham, relatively close. Livingston County essentially consists of the exurban communities between Detroit and Lansing, and Slotkin has held the GOP margin there to under 20 points. The Crystal Ball is starting the open MI-7 race as a Toss-up.
The last time Michigan saw an open-seat Senate contest, in 2014, now-Sen. Gary Peters (D-MI) had no opposition to succeed the late Sen. Carl Levin (D-MI). A competitive primary may force Democratic contenders to better establish themselves with Black voters, although any statewide Democratic campaign in Michigan worth its salt should emphasize outreach to minorities. At the time of his election to the Senate, Peters was in the odd position of being a white member who represented a Black-majority House district — the credibility that he established with the Black community likely helped him in 2014 and 2020. Slotkin’s district is only about 7% Black by composition, a number half the statewide 14%, so look for her campaign to aggressively court that key demographic.
McClellan enjoys broad-based overperformance
Speaking of majority-minority districts, let’s take a quick detour to our home state. Last week, we wrote about the special election in the 4th District, a heavily Black seat that elected Rep.-elect Jennifer McClellan (D), who will be leaving the state Senate to enter the U.S. House. McClellan’s victory was not a surprise but her margin was — her roughly 3-to-1 edge was notably better than what most Democrats get in the district.
Turnout dynamics often are different in special elections than typical general elections, which sometimes accounts for odd partisan results. In one fairly recent example, Louisiana had a special election for state treasurer in 2017. The treasurer runoff election was held concurrently with a mayoral runoff in heavily Democratic New Orleans. With the mayoral election on the ballot, Orleans Parish cast close to a quarter of the votes in the statewide treasurer’s race (the parish usually casts more like 10% of the state’s votes). With New Orleans exerting a disproportionate influence, the Democratic nominee for treasurer, Derrick Edwards, took close to 45% against now-Treasurer John Schroder (R). Considering the lean of the state and his lack of funding, Edwards’s showing was respectable. But when the office was up again, in the regularly-scheduled 2019 election, things looked more typical — Schroder was reelected by 25 points.
Along those lines, we wondered if McClellan’s margin was padded by a disproportionately strong showing in her home area, Richmond. As it turns out, that wasn’t really the case. Richmond City and neighboring Henrico County are 2 of the largest, and bluest, localities in the district. Last week, the pair cast exactly half the total vote in the election — that was up only slightly from the 49% they accounted for in 2022. So McClellan’s showing was more of a broad-based overperformance than anything else.
As a bit of a thought experiment, we took the 2022 result from the 4th District and applied a uniform swing. In other words, last year, the late Donald McEachin (D) was reelected by 30.1 points; last week, McClellan did 18.9 points better, winning by 49%. How would an across the board 18.9% swing towards Democrats compare the actual result? Table 1 considers this.
Table 1: 2022 uniform swing vs actual 2023 result in VA-4
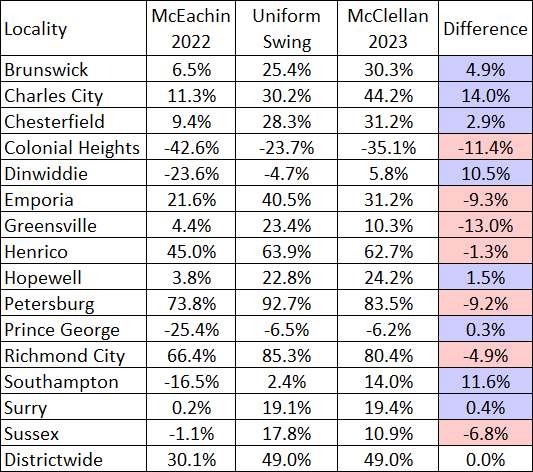
As it turned out, McClellan ran slightly behind “expectations” in both Richmond and Henrico, although she obviously carried them overwhelmingly. Her biggest overperformance was actually from another locality that she currently represents in the state Senate: Charles City. One of the smaller counties in the district (it only has 3 voting precincts), it was the commonwealth’s most Democratic county in 1990s-era presidential elections, but its blue lean has eroded in recent years. McClellan’s 44-point margin there was 33 points better than what McEachin earned, and 14 points more than what a uniform swing would suggest.
McClellan ran ahead of expectations in several rural Southside counties, one of which was Surry. Just south of Charles City County, Surry County has been undergoing similar larger-scale trends. In 2021, now-Gov. Glenn Youngkin became the first modern GOP nominee for governor to carry this historically deep blue locality (although he did so by just 12 votes).
When McClellan is next on the ballot, in 2024, it seems likely that she’ll have a more “typical” Democratic coalition. Next year, a much larger presidential electorate may be in a more straight-ticket mood. The 110,000 votes that were cast in last week’s election represent just a quarter of the nearly 400,000 ballots the district would have cast in the 2020 election. Still, we’ll be watching to see how McClellan’s initial rural appeal translates with an election held under more “normal” circumstances.